Show summary Hide summary
- High-speed rail and the energy math of smart corridors
- Smart cities, data and the politics of digital transformation
- Water stress, climate risk and the hidden smart city crisis
- Housing, junk fees and the smart city equity gap
- Where mobility, climate and smart infrastructure meet
- From pilot lanes to climate‑aligned transport networks
- Key smart cities insights you can apply now
- Why does California’s high-speed rail matter for smart cities?
- How are smart cities related to climate and energy transition?
- What role does data transparency play in urban innovation?
- Can smart infrastructure help rural and peri-urban communities?
- Where can professionals follow more smart cities reporting?
Five stories, five turning points: a $1 billion-a-year bet on high‑speed rail, water systems on the brink, junk fees reshaping housing, and data‑driven streets quietly redefining what smart cities really mean for your commute, your bills and your climate footprint.
Across these narratives, smart cities stop being buzzwords and become infrastructure decisions with deadlines, dollar signs and carbon impacts attached. From California’s embattled rail line to rental reforms and global water stress, the most compelling pieces from Smart Cities Dive trace how urban innovation is colliding with climate reality, equity demands and tight public budgets.
High-speed rail and the energy math of smart corridors
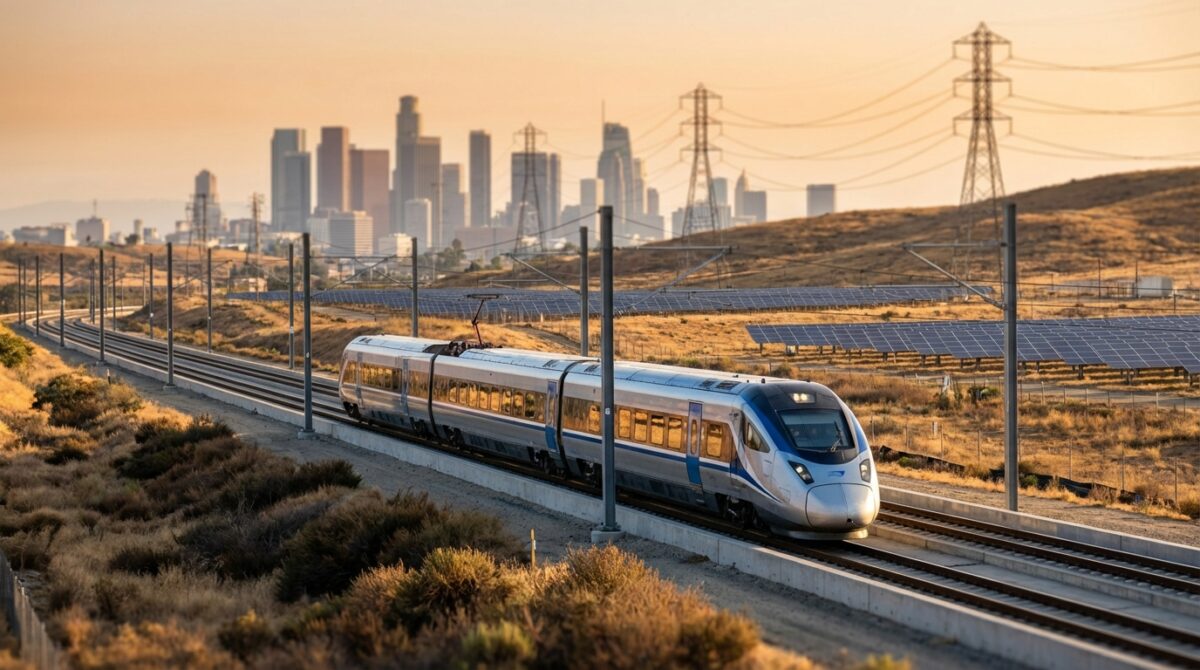
At the center of this year’s coverage stands California’s high‑speed rail saga, a project with clear implications for sustainability, energy use and regional planning. Approved in 2008 to link San Francisco and Los Angeles, the electrified line promises to shift millions of trips from planes and cars to a grid‑powered system with far lower emissions per passenger‑kilometer.
Remote Work and Severe Weather Drastically Transform Urban Traffic Dynamics
14 insightful forecasts shaping the future of cities by 2026

Financing a climate-aligned mobility backbone
When Ian Choudri took over the California High-Speed Rail Authority in August 2024, he inherited delays, political crossfire and a project fighting to keep its climate case alive. The legislature’s decision to direct $1 billion a year for 20 years created a predictable funding spine, allowing the authority to plan for 120 miles of completed civil works by the end of 2026 and track‑laying starting next year.
That corridor is more than tracks. Choudri’s team is pitching it as a smart infrastructure spine, exploring fiber and 5G concessions for hyperscale cloud providers such as Google and Meta, turning a rail right‑of‑way into a multi‑service asset. Every kilometer that carries both passengers and data nudges California closer to the vision explored daily on Smart Cities Dive: transport, IoT and energy systems converging rather than competing.
Smart cities, data and the politics of digital transformation
Beyond trains, Smart Cities Dive’s most-read coverage tracks how data analytics is seeping into everything from traffic lights to tenant protection. Urban leaders are no longer asking whether to embrace digital tools, but how fast and on whose terms. Readers who follow curated roundups such as What we are reading see that struggle play out across continents.
From pilot projects to citywide operating systems
Stories highlighted in collections like top 5 stories from Smart Cities Dive show a pattern: cities moving from scattered pilots to integrated platforms. Sensors once used only to time traffic lights now feed into broader urban planning dashboards that track emissions, congestion and even heat exposure street by street.
This pivot demands new skills inside city halls. Engineers trained on roads and sewers now broker contracts about data ownership and algorithm transparency. For professionals trying to keep up with that shift, profiles of Smart Cities Dive’s newsroom underline how journalism has become part of the smart infrastructure ecosystem, translating code and contracts into consequences for residents.
Water stress, climate risk and the hidden smart city crisis
One of the most urgent threads running through current coverage is water. While shiny renderings of future cities tend to highlight rooftop gardens and autonomous shuttles, underground networks tell a tenser story. Research shared in analyses such as the UN’s warning on a looming global water bankruptcy puts cities at the front line of climate‑driven scarcity.
Digital monitoring for leaking, sinking and drying systems
Smart water meters, pressure sensors and satellite‑based leak detection now feature as prominently in future cities strategies as mobility apps. For utilities serving millions, fine‑grained data means spotting leaks before roads collapse or aquifers are overdrawn. That is climate adaptation in practice, often cheaper than new dams or desalination plants.
Coverage across platforms like SmartCitiesWorld’s top news stories and the broader smart cities conversations on Medium shows how fast these tools are scaling. Yet every sensor invites questions: who pays, who controls the data and how are low‑income neighborhoods protected from service shutoffs when every liter is monitored?
Housing, junk fees and the smart city equity gap
Technological progress loses credibility when residents are priced out of the places it is meant to improve. That tension sits at the heart of another widely shared storyline: new rules targeting junk fees in rental housing and municipal services. Coverage of policies aimed at scrapping rental junk fees reframes smart cities as a question of fairness, not only hardware.
Data transparency as an affordability tool
Digital portals now allow tenants to see every charge levied by landlords or city agencies in one interface. When paired with open data requirements, these tools expose patterns of overcharging and enable regulators to act. For families living near new transit lines or upgraded districts, such transparency can mean the difference between benefiting from urban innovation or being displaced by it.
Initiatives documented in collections like 33 stories to learn about smart cities show how activists, planners and coders collaborate on these affordability dashboards. The underlying insight is simple: if sensors make streets smarter, billing systems shouldn’t stay opaque.
Where mobility, climate and smart infrastructure meet
The energy transition threads through nearly every high-impact story from Smart Cities Dive. Electric buses, congestion pricing and ambitious rail schemes together redraw the emissions profile of metropolitan regions. Debates around car‑free events in major cities, such as the discussion highlighted in this Los Angeles car‑free proposal, make that connection visible on city streets.
From pilot lanes to climate‑aligned transport networks
Integrated transport planning now treats stations as energy and data hubs, not only boarding points. In California’s Central Valley, planners are already exploring how electrified freight trains on the high‑speed corridor could offer farmers a lower‑carbon, cheaper alternative to trucking produce to ports and cities. That shift would cut diesel use, improve air quality and support rural economies.
For readers tracking these converging agendas, streams such as the best of Smart Cities Dive and the social feed of Smart Cities Dive on Facebook function as an evolving atlas. Together they chart how technology choices in one corridor or neighborhood shape emissions curves, public health and economic opportunity for decades.
Key smart cities insights you can apply now
Across these top stories, several patterns emerge that any practitioner, student or resident can translate into action:
- Treat corridors as multi‑service assets: combine transport, smart infrastructure, fiber and clean energy on the same routes.
- Insist on data transparency: whether for water, mobility or rent, accessible information is a climate and equity tool.
- Plan with climate timelines in mind: align rail, housing and water investments with 2030 and 2050 decarbonization goals.
- Center vulnerable communities: design digital transformation to lower bills and risks for those most exposed.
- Watch how pilots scale: the real test is whether small projects become resilient, citywide systems.
Taken together, these lessons show why smart cities coverage on platforms like Smart Cities Dive matters far beyond the tech sector. Each story is a snapshot of how climate targets, infrastructure finance and everyday urban life are being rewired in real time.
Why does California’s high-speed rail matter for smart cities?
The project is more than a transport upgrade. It combines electrified mobility, potential fiber and 5G routes, and opportunities for cleaner freight. If completed as planned, it would shift trips from cars and planes to grid-powered trains, cutting emissions while creating a smart corridor that carries people, data and energy together.
How are smart cities related to climate and energy transition?
Smart cities use sensors, data analytics and connected infrastructure to manage energy, water, transport and buildings more efficiently. When aligned with decarbonization goals, these tools help lower emissions, integrate renewables, reduce waste and support adaptation to extreme heat, drought and floods, turning technology into a practical climate strategy.
What role does data transparency play in urban innovation?
Transparent data on rents, utility use, traffic or pollution allows residents and regulators to spot unfair practices, target investments and evaluate policies. It shifts power from closed systems toward accountable decision-making, making digital tools supportive of equity rather than drivers of hidden costs or exclusion.
Can smart infrastructure help rural and peri-urban communities?
Yes. Corridors built for high-speed passenger rail, broadband or clean energy can also serve farmers, small towns and logistics hubs. For example, electrified freight on a high-speed line could lower shipping costs and emissions for agricultural regions, while shared fiber routes expand connectivity beyond city centers.
Where can professionals follow more smart cities reporting?
Congress Moves Forward with New Transportation Funding Legislation
New Federal Bill Proposes Restrictions on City and State Control Over Autonomous Vehicles
Professionals can follow in-depth coverage on Smart Cities Dive’s main site, explore curated roundups of what editors are reading, and consult collections such as top-trending smart cities stories or long-form explainers on platforms like Medium and HackerNoon, which often cross-reference Smart Cities Dive’s reporting.